Deliverables on Overhead
Recent deliverables on distribution overhead assets are highlighted below.
2020

Overhead Line Performance: Pole-Top Splitting and Aged Crossarm Performance
This research examined the performance of the pole top and addressed the research questions: How do bolts in the pole top cause splitting and what parameters make splitting more likely? What is the remaining vertical strength of wood crossarms that have been in service? Can hyperspectral imaging, a nascent technology, help utilities estimate remaining wood crossarm strength.

Alternative Pole and Crossarm Material Evaluation: 2020 Update
Research in 2020 focused on measuring the strength of composite materials in extreme temperatures, from -40°F (-40°C) to 140°F (60°C), reviewing composite materials subjected to ongoing accelerated aging, and investigating the use of hyperspectral cameras as an inspection tool.
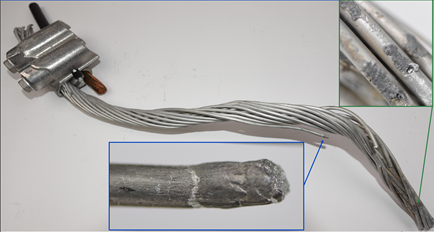
Overhead Connector Performance: Laboratory Testing and Forensic Analysis
This report provides the forensic analyses of two failed automatic splices and a wedge connector. Overhead connector fault testing also began in 2020. This testing will continue into 2021 and will inform how overhead connectors age and potentially degrade as they are exposed to load cycling and faults.
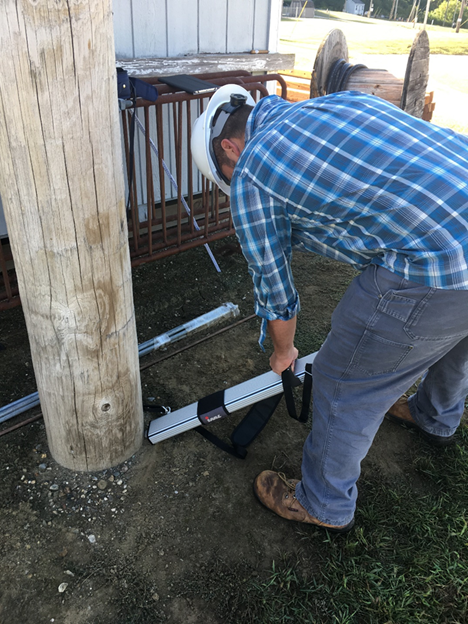

Evaluation of Pole Inspection Technologies: 2020 Research Update
This study examined the effectiveness of the IML Resistograph by using the tool on utility provided poles and then measuring the actual remaining strength through destructive testing. Overall, the tool was effective at identifying groundline decay and cavities, though many pole failures occurred above groundline during testing.

Online Monitoring of Overhead Distribution Systems: State of the Technology and Case Studies
One nascent overhead distribution inspection approach is to deploy monitors that are capable of detecting and reporting incipient faults and partial discharges. Available technologies can provide enough information to help identify the type of defect, that is, broken conductor strands or internal transformer degradation. These monitors can also be deployed as a mesh network to help locate degrading assets. The potential benefit of these devices is that they provide situational awareness to utilities, reducing the need for inspections and identifying problems that may not be visually apparent before failure occurs. However, there is also a risk that issues that do not require imminent repair or replacement will also be identified, causing utilities to spend O&M budgets on nonessential repairs. The Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) is planning to evaluate the effectiveness of these technologies in a laboratory setting, document pilot demonstrations, and provide utility support through failure analysis to help utilities associate electrical signatures with failure modes.
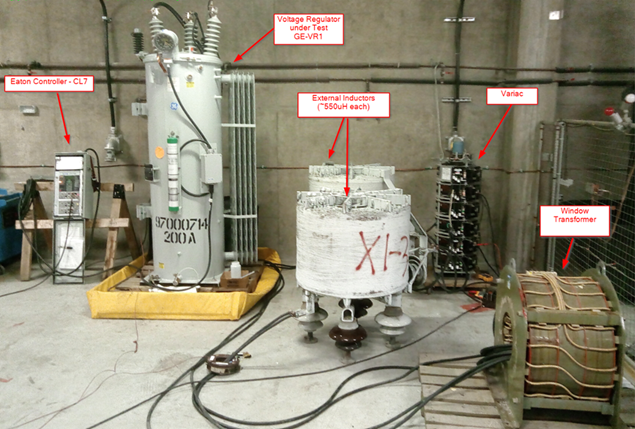
Investigation of Frequent Tap Changes in Voltage Regulators: Switching Cycle Test
This testing investigated the aging characteristics of a voltage regulator subjected to frequent operation and examined the effectiveness of inspection and maintenance procedures. Specifically, dissolved gas analysis (DGA) monitoring is one option that could indicate the need for maintenance, but the relationship between DGA analysis and the condition of the voltage regulators to be examined is not well understood. The results from this research are helping to elucidate that relationship.

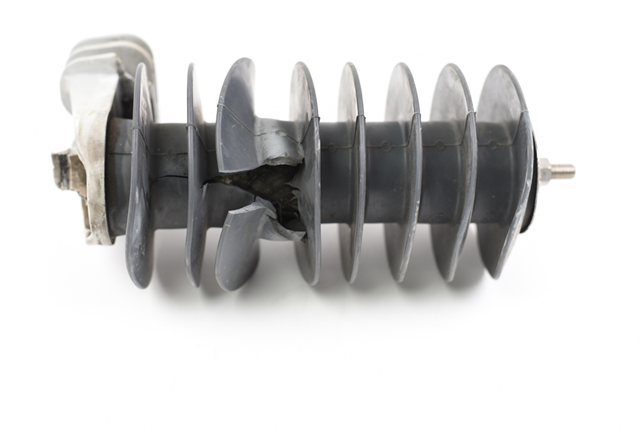
Design and Application of Wildlife Guards to Promote Reliability: 2020 Research Update
EPRI conducted testing and analyses of many bushing type wildlife guards, including material analyses, arcing exposure response, dielectric puncture strength, aging tests, and tests of incorrect installation. Material analyses identified the base polymers and key ingredients included within the different guards, including flame retardants, UV inhibitors, and antioxidants. Arc testing examined the flammability and durability of wildlife guards subjected to a flashover that might be experienced on distribution systems. Dielectric puncture strength investigated the ability of the wildlife guard materials to withstand full voltage application across the polymer alone.

Animal-Caused Outage Prevention Products: Effectiveness and Durability — A Framework for Product Testing
This report provides an inclusive list of 347 commercially available products designed to mitigate animal-caused outages on overhead distribution and transmission lines and in substations. Based on reported problems and field experience, three modes of animal-caused outage mitigation device failures have been previously defined: engineering failures, efficacy failures, and implementation failures. This report lists recommended tests to identify device shortcomings for each mode of failure for each device, based on the scientific literature, industry reports, and professional experience.

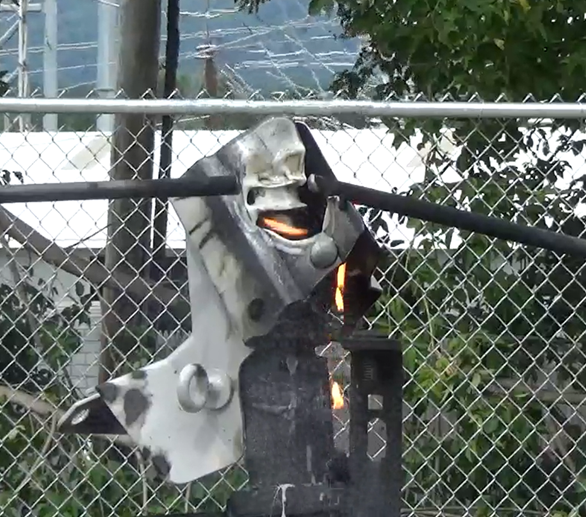
Evaluation of Surge Arrester Performance: Aging Test Results and MOV Analysis
In 2020, the research investigated the performance of a distribution surge arrester subjected to a novel test exposing it to 115°C steam while energized. This multi-stress test examines the arrester’s propensity for thermal runaway by monitoring watts loss as well as susceptibility to moisture ingress. Additionally, a utility submitted two surge arresters for failure analysis; the units failed in service after two years. The results of those analyses are reported upon herein.
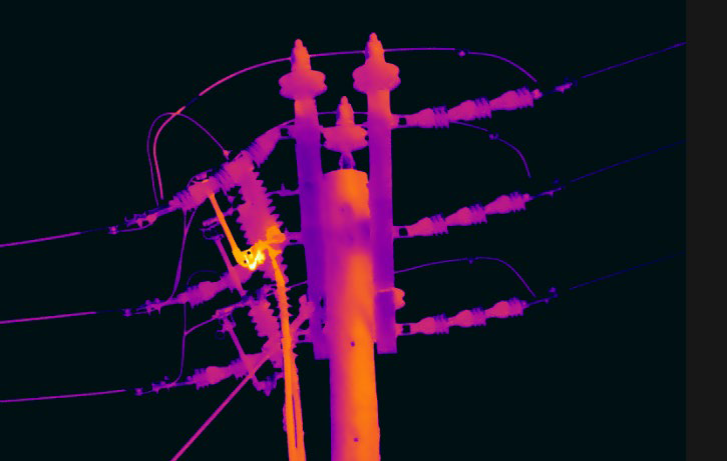
Overhead Distribution Infrared Inspection Guidebook: 2020 Update
This guidebook presents a comprehensive review of infrared inspection on distribution systems. This work first provides a background on infrared science and technology to help educate new engineers or technicians and to elucidate the camera selection process. Inspection programs are discussed in terms of structure, and cost avoidance calculations are addressed. Training and certification are reviewed, as well as severity criteria options. Targeted lab tests were performed to study the thermal characteristics of various distribution components to determine normal and abnormal operating temperatures.